已知一个有序矩阵mat,同时给定矩阵的大小n和m以及需要查找的元素x,且矩阵的行和列都是从小到大有序的。设计查找算法返回所查找元素的二元数组,代表该元素的行号和列号(均从零开始)。保证元素互异。
数据范围: ,矩阵中的任何元素满足
,矩阵中的任何元素满足 
要求:空间复杂度 ) ,时间复杂度
,时间复杂度 )
[[1,2,3],[4,5,6]],2,3,6
[1,2]
[[1,2,3]],1,3,2
[0,1]
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
public int[] findElement(int[][] mat, int n, int m, int x) {
// write code here
int i = 0;
int j = m - 1;
while (i < n && j >= 0) {
if (mat[i][j] > x) {
j--;
} else if (mat[i][j] < x) {
i++;
} else {
break;
}
}
return new int[] {i, j};
}
}
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
public int[] findElement(int[][] mat, int n, int m, int x) {
//为了个人的阅读方面,令m代表行,n代表列
int tmp=n;
n=m;m=tmp;
int [] res=new int[2];
//从右上角开始,如果x大于该数,则下移,若小于则右移
int i=0,j=n-1;
while(i<m&&j>=0)
{
if(x>mat[i][j])i++;
else if(x<mat[i][j])j--;
else{
res[0]=i;
res[1]=j;
break;
}
}
return res;
}
} public int[] findElement(int[][] mat, int n, int m, int x) {
// write code here
int row = n - 1;
int col = 0;
while (col < m && mat[row][col] < x) {
col++;
}
if (mat[row][col] < x) {
return new int[]{-1, -1};
}
while (row >= 0 && mat[row][col] > x) {
row--;
}
return new int[]{row, col};
} import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
public int[] findElement(int[][] mat, int n, int m, int x) {
// write code here
//从右上角开始查找
int[] ans=new int[2];
for(int i=0;i<n;){
for(int j=m-1;j>=0;){
if(mat[i][j]<x) i++;
else if(mat[i][j]>x) j--;
else {ans[0]=i;ans[1]=j;return ans;}
}
}
return ans;
}
} class Solution {
public:
vector<int> findElement(vector<vector<int> > mat, int n, int m, int x) {
vector<int> v;
if(n==0 || m==0)
return v;
int i=0,j=m-1;
while(i<n && j>=0){
if(mat[i][j]==x){
v.push_back(i);
v.push_back(j);
return v; }else if(mat[i][j]<x) i++; else j--; } return v;
}
};
//思路和评论做多的答主思路一致
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> findElement(vector<vector<int> > mat, int n, int m, int x) {
// write code here
int row = 0;
int col = m - 1;
while (row < n && col >= 0){
if (mat[row][col] == x)
return{ row, col };
else if (mat[row][col] < x)
row++;
else
col--;
}
return{ -1, -1 };
}
};
尾部不断缩小的二分查找 class Solution {public:vector<int> findElement(vector<vector<int>> mat, intn, intm, intx){for(inti = 0; i < n; ++i){if(mat[i][0] <= x && mat[i][m - 1] >= x){intpos = lower_bound(mat[i].begin(), mat[i].end(), x) - mat[i].begin();if(mat[i][pos] == x) returnvector<int>{i,pos};elsem = pos;}}returnvector<int>{-1, -1};}};
//从右上角开始,如果x大于mat[row][col],则下移一行; //如果x小于mat[row][col],则左移动一列 import java.util.*; public class Solution { public int[] findElement(int[][] mat, int n, int m, int x) { if(mat == null || mat.length != n || mat[0].length != m){ return null; } int row = 0, col = m - 1; while(row < n && col >= 0){ if(mat[row][col] == x){ return new int[]{row, col}; }else if(mat[row][col] < x){ row++; }else{ col--; } } return null; } }
//与剑指offer中第一题一样
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
public int[] findElement(int[][] mat, int n, int m, int x) {
// write code here
if(n==0 || m==0)
return new int [0];
int []re=null;
int x0=0;
int y0=m-1;
while(x0<mat.length&&y0>=0){
if(mat[x0][y0]==x){
re=new int[2];
re[0]=x0;
re[1]=y0;
break;
}else if(mat[x0][y0]<x){
x0++;
}else{
y0--;
}
}
if(re==null){
return new int[0];
}else{
return re;
}
}
}
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
class Solution:
def findElement(self, mat, n, m, x):
if n < 1 and m < 1:
return []
i = 0
j = m - 1
while i < n and j >= 0:
if mat[i][j] == x:
return [i, j]
elif mat[i][j] < x:
i += 1
else:
j -=1
return []
//《剑指offer》里面的题目,思路一样;
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> findElement(vector<vector<int> > mat, int n, int m, int x)
{
// write code here
vector<int> vec;
if(n<=0 ||m<=0) return vec;
int start=0;
int end=m-1;
while(start<n && end>=0)
{
if(mat[start][end]==x)
{
vec.push_back(start);
vec.push_back(end);
break;
}
else if(mat[start][end]<x)
{
++start;
}
else if(mat[start][end]>x)
{
--end;
}
}
return vec;
}
};
// write code here
if(mat == null || mat.length != n || mat[0].length != m){
return null;
}
int row = 0, col = mat[0].length-1;
while(row <= mat.length-1 && col >= 0){
if(mat[row][col] == x){
return new int[]{row, col};
}else if(mat[row][col] > x){
col--;
}else{
row++;
}
}
return null;
}
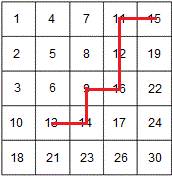
从右上角开始,每次将搜索值与右上角的值比较,如果大于右上角的值,则直接去除1行,否则,则去掉1列。如下图显示了查找13的轨迹。首先与右上角15比较,13<15,所以去掉最右1列,然后与11比较,这是13>11,去掉最上面1行…以此类推,最后找到13。算法复杂度O(n),最坏情况需要2n步,即从右上角开始查找,而要查找的目标值在左下角的时候。
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> findElement(vector<vector<int> > matrix, int row, int col, int x) {
vector<int> result;
if(row == 0 || col == 0){
return result;
}//if
int i = 0,j = col - 1;
while(i < row && j >= 0){
// 大于目标 剔除这个数字所在的列
if(matrix[i][j] > x){
--j;
}//if
// 小于目标 剔除这个数字所在的行
else if(matrix[i][j] < x){
++i;
}//else
else{
result.push_back(i);
result.push_back(j);
return result;
}//else
}//while
return result;
}
};
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> findElement(vector<vector<int> > mat, int n, int m, int x) {
// write code here
vector<int>re;
if (n==0||m==0)return re;
int row=0,col=m-1;
while(row<n&&col>=0)
{
if (mat[row][col]<x)row++;
else if(mat[row][col]>x)col--;
else
{
re.push_back(row);
re.push_back(col);
return re;
}
}
return re;
}
}; import java.util.*;
/*
思路:这题目的意思应该是从第一列第一个到最后一列最后一个都是有序的,不然如果只是单行有序的话就要麻烦很多了
可以分析最右上角的元素,如果这个元素大于所查找的,那必然在最右上角元素的左边即列-1,如果小于,行+1
我本来想递归的,但是从右上角开始做递归要新建一个函数,还要设置约束条件- -贼麻烦
*/
public class Solution {
public int[] findElement(int[][] mat, int n, int m, int x) {
int i=0;
int j=m-1;
int[] goal=new int[2];
while(i<n&&j>=0){
if(mat[i][j]==x){
goal[0]=i;
goal[1]=j;
break;
}
else if(mat[i][j]>x) j--;
else i++;
}
return goal;
}
}
运行时间:208ms
占用内存:15224k
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
public int[] findElement(int[][] mat, int n, int m, int x) {
// write code here
int i = 0;
int j = m -1;
while(i<n && j>=0){
if(mat[i][j] == x)
return new int[]{i,j};
if(mat[i][j] <x){
i = i + 1;// 行增加
}else{
j = j - 1;// 列减少
}
}
return new int[]{-1,-1};
}
public int[] findE(int[][] A,int i,int j,int n,int m,int x){
if(A[i][j] == x)
return new int[]{i,j};
if(i<0 ||j<0 ||i>=n ||j>=m)
return new int[]{-1,-1};
if(A[i][j] <x)
return findE(A,i+1,j,n,m,x);
return findE(A,i,j-1,n,m,x);
}
}